Problem:
How can multinational companies ensure that their market research is both accurate and culturally relevant across different countries? Why do some businesses fail when expanding into new markets despite thorough research? How do language and cultural nuances impact data collection and interpretation?
In international market research, these questions are critical. Research that fails to account for cross-cultural differences in language, perception, and response patterns can lead to misleading conclusions and costly mistakes.
Background:
Despite recent geopolitical shifts—such as rising nationalism, trade tensions, and conflicts affecting global stability, including the imposition of tariffs at levels unseen in recent decades—we still live in an interconnected world where multinational companies find significant opportunities for expansion beyond their domestic markets. The growth of market economies, coupled with rising demand from the emerging middle classes and rapid technological advancements, has facilitated access to new markets. Consequently, a substantial portion of many companies’ revenue is generated internationally.
These developments have profound implications for the market research industry. Practitioners seek guidance on the applicability of home market marketing strategies (e.g., market orientation, consumer behavior, and advertising effectiveness) in diverse national contexts. High-profile failures underscore the critical importance of understanding and adapting to local markets. These setbacks are often attributed to failure to grasp the nuances of the new context and to tailor marketing activities appropriately.
To provide valuable recommendations, marketing science must move beyond single-country studies. Multi-country research, involving data collection in two or more nations, is essential for identifying both the generalizable similarities and the crucial differences in market-related insights across countries. These insights serve as vital guidelines for international marketing decisions.
While multi-country research shares commonalities with single-country projects (e.g., the use of primary and secondary data), it presents additional complexities. From the initial conceptual design to data collection, analysis, and interpretation, researchers must navigate numerous pitfalls to ensure the validity and utility of international marketing studies. For example, if we are looking at how people feel about a product, we need to make sure we are measuring the same thing in each country, even if the words or ideas are slightly different. If we do not, we might think we see a real difference when it is just a problem with our research. Moreover, language and cultural nuances can significantly impact data quality, making accurate and context-aware translation a critical step before fielding a study. In this article, we explore the importance of translation in research, the subtle ways language and culture shape responses, and how Kalever’s AI-based tools help optimize this process—ensuring clarity, consistency, and efficiency across markets.
The Critical Role of Translation and the Power of AI
Collecting data in multiple languages necessitates ensuring translation equivalence. The dominant approach in international marketing studies is back-translation. This involves translating a questionnaire into another language by a bilingual person and then back-translating it to the original language by another bilingual person. Equivalence is assumed only when there are no relevant differences between the original and back-translated questionnaires.
How It Works?
- Initial Translation: A bilingual translator translates the questionnaire from the original language (e.g., English) into the target language (e.g., Dutch).
- Back-Translation: A different bilingual person, who has not seen the original questionnaire, translates the new version back into the original language.
- Comparison: The original and back-translated versions are compared to check for discrepancies. If there are major differences, the translation is revised to better capture the intended meaning.
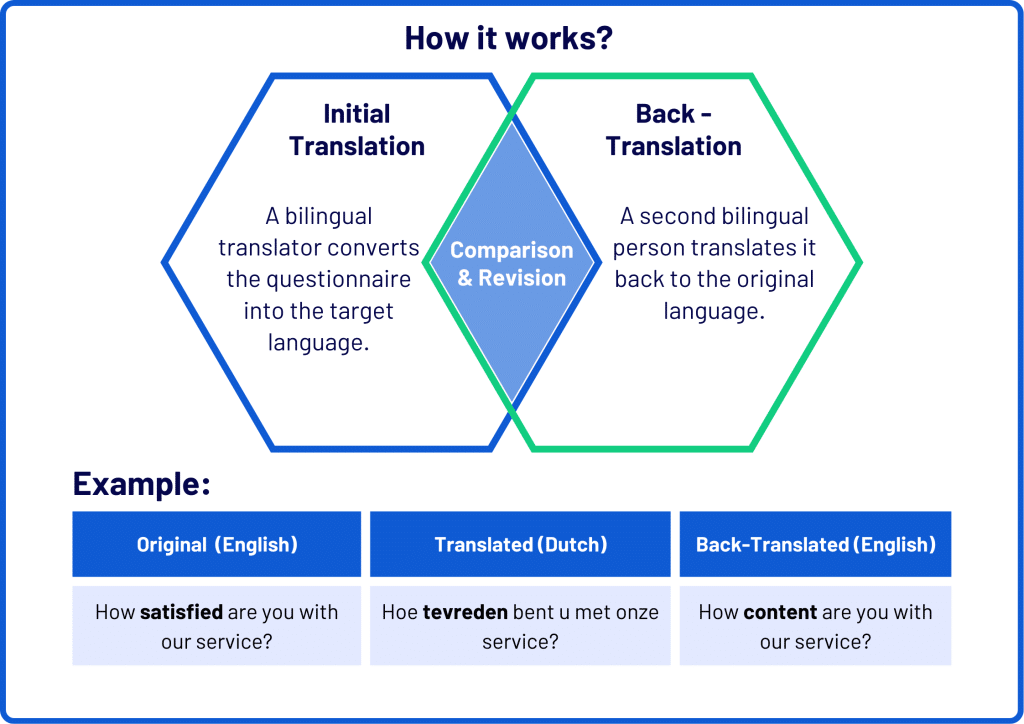
In this case, “content” and “satisfied” are close in meaning, but “content” might suggest a lower level of satisfaction than “satisfied.” If the research requires precise wording, the Dutch translation might need slight adjustments to ensure it fully captures the intended meaning of “satisfied.” This process helps prevent misinterpretations and ensures that the translated questionnaire measures the same concepts as the original.
While widely used, back-translation has limitations, as it does not always guarantee equivalence in meaning. We at Kalever believe that a good translation process should involve multiple translators who pay close attention to items related to attitudes, as linguistic research indicates that word connotations can vary across languages. Often in our studies, we come across a common challenge when translating multi-item measures that include both positively and negatively worded statements. These mixed-worded scales can behave unpredictably when used across different countries. Research has shown that they sometimes lose their internal consistency or fail to measure what they are intended to.
Why does this happen? There are two key reasons:
- Languages handle negation in different ways. A phrase that is straightforward in one language might become confusing or even take on a different meaning when translated.
- Cultural differences play a role. Some respondents tend to react differently to negatively worded statements, either interpreting them in unexpected ways or showing a bias toward agreeing with statements in general.
For example, imagine a survey measuring job satisfaction. In English, we might ask:
- “I enjoy my work.” (positive)
- “I do not feel valued at work.” (negative)
When translated, the second statement might not carry the same weight or clarity in another language, leading to inconsistent responses. Additionally, in some cultures, people tend to agree with statements out of politeness or social norms, affecting the accuracy of the results.
This is why translating such measures requires extra care—not just direct translation, but cultural and linguistic adaptation to ensure the questions truly capture what they are meant to measure.
Solution: Kalever’s AI-Powered Solution for Streamlined and Accurate Translation
Traditional translation methods, like back-translation, can be time-consuming, expensive, and prone to error. They often involve multiple rounds of translation and back-translation, which can significantly delay the research process. Kalever’s AI-based automatic translation tool offers a solution to these challenges. By leveraging advanced artificial intelligence, our technology can significantly speed up and improve the translation of international market research materials. The key benefits of using our tool include increased efficiency, enhanced accuracy, and a deep understanding of contextual nuances, all of which work together to provide seamless and cost-effective translations.
Key benefits of Kalever’s AI translation tool:
- Speed and Efficiency: AI-powered translation can translate large volumes of text in a fraction of the time required by traditional methods, accelerating the research process.
- Accuracy and Consistency: Our AI algorithms are trained on vast datasets of research documents across various topics and languages. This enables the tool to identify and address nuanced linguistic differences, ensuring greater accuracy and consistency in translation.
- Contextual Understanding: Kalever’s technology goes beyond simple word-for-word translation. It considers the context of the text, including cultural nuances and industry-specific terminology, to provide more accurate and relevant translations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Automating the translation process with AI can significantly reduce the costs associated with traditional translation services.
- Expertise and Partnership: In addition to our technological capabilities, we offer the expertise of our team and partners who can provide the right approach for each country and target group. Our partners are directly integrated into our platform and trained to work seamlessly within it, enabling translations at unimaginable speed and accuracy. Combining linguistic and cultural knowledge we make sure that research is both accurate and locally relevant. At the same time, we offer flexibility—if our clients prefer, their own team can make final refinements to ensure the research aligns perfectly with their specific needs.
By leveraging AI, Kalever helps researchers overcome the challenges of cross-cultural communication, enabling them to conduct more efficient, accurate, and insightful international market research. This ultimately leads to better decision-making and greater success in global markets.
Conclusion
Conducting international market research presents a complex set of challenges, particularly in ensuring translation equivalence. However, advancements in AI-driven translation technology offer powerful tools to overcome these hurdles. By leveraging solutions like Kalever’s AI translation tool, researchers can streamline the translation process, enhance accuracy, and gain deeper, more reliable insights into global markets. This ultimately empowers businesses to make informed decisions and thrive in the international arena
